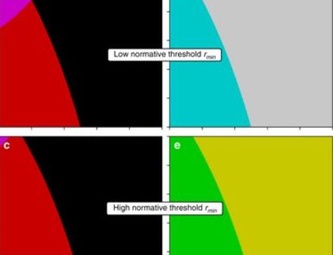
Better be safe than sorry: economic optimization risks tipping of important Earth system elements
06/15/2018 - Optimizing economic welfare without constraints might put human well-being at risk, a new climate study argues. While being successful in bringing down costs of greenhouse gas reductions for instance, the concept of profit maximization alone does not suffice to avoid the tipping of critical elements in the Earth system which could lead to dramatic changes of our livelihood. The scientists use mathematical experiments to compare economic optimization to the governance concepts of sustainability and the more recent approach of a safe operating space for humanity. All of these turn out to have their benefits and deficits, yet the profit-maximizing approach shows the greatest likelihood of producing outcomes that harm people or the environment.
Read More
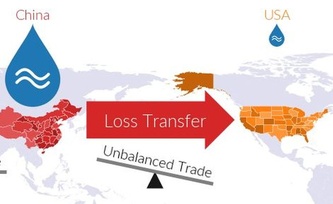
China floods to hit US economy: climate effects through trade chains
05/28/2018 - Intensifying river floods could lead to regional production losses worldwide caused by global warming. This might not only hamper local economies around the globe – the effects might also propagate through the global network of trade and supply chains, a study now published in Nature Climate Change shows. It is the first to assess this effect for flooding on a global scale, using a newly developed dynamic economic model. It finds that economic flood damages in China, which could, without further adaption, increase by 80 percent within the next 20 years, might also affect EU and US industries. The US economy might be specifically vulnerable due to its unbalanced trade relation with China. Contrary to US president Trump’s current tariff sanctions, the study suggests that building stronger and thus more balanced trade relations might be a useful strategy to mitigate economic losses caused by intensifying weather extremes.
Read More
Social and Natural science together: New Co-Directors to lead the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
23/02/2018 - The Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) is reinventing itself – appointing a twin leadership bringing together natural sciences and social sciences stronger than ever. In late September, the German climate economist Ottmar Edenhofer and the Swedish Earth system scientist Johan Rockström will become directors of the internationally renowned institute which is a member of the Leibniz Association. This was decided on Friday by the institute's Board of Trustees, headed by the Brandenburg Ministry of Science, Research and Culture and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. The retirement of the founding director Hans Joachim Schellnhuber this autumn after a quarter of a century as the head of the institute marks the beginning of a new era in Potsdam.
Read More
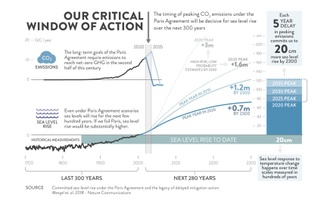
Sea-level legacy: 20cm more rise by 2300 for each 5-year delay in peaking emissions
02/20/2018 - Peaking global CO2 emissions as soon as possible is crucial for limiting the risks of sea-level rise, even if global warming is limited to well below 2°C. A study now published in the journal Nature Communications analyzes for the first time the sea-level legacy until 2300 within the constraints of the Paris Agreement. Their central projections indicate global sea-level rise between 0.7m and 1.2m until 2300 with Paris put fully into practice. As emissions in the second half of this century are already outlined by the Paris goals, the variations in greenhouse-gas emissions before 2050 will be the major leverage for future sea levels. The researchers find that each five year delay in peaking global CO2 emissions will likely increase median sea-level rise estimates for 2300 by 20 centimeters.
Read More
New book: Water - scarcity, climate change and world nutrition by Dieter Gerten
"Century drought in Australia", "Mexico City is running dry" or "Groundwater resources are drying up" - headlines like these illustrate that a global era of water scarcity seems to have begun. Water crises have become a major global risk for the economy and society. At the same time, a United Nation's World Water Report estimates that the global water demand is to increase by more than half until 2050. "Water - scarcity, climate change and world nutrition", the new book by Dieter Gerten from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), just published by C.H.Beck Verlag, analyses the alleged global water crisis against the background of climate change and the further increase in demand for food.
Read More
Biomass plantations not compatible with planetary boundaries
01/22/2018 - Planting trees or grasses on a grand scale in plantations to extract CO2 from the atmosphere - this could make a long-term contribution to climate protection, but it would push the planet beyond ecological limits in other dimensions. A new study by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) in the journal Nature Climate Change now for the first time establishes a connection between ambitious international climate objectives and the more comprehensive concept of planetary boundaries. If biomass plantations in which plants bind carbon dioxide during growth are massively expanded, this would entail enormous risks for areas that are already stressed, such as biodiversity, biogeochemical flows, water resources and land use. According to the study, biomass as a means to capture and store CO2 can therefore only make a limited contribution. In order to stabilize the climate, a rapid reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from the combustion of coal, oil and gas is crucial.
Read More