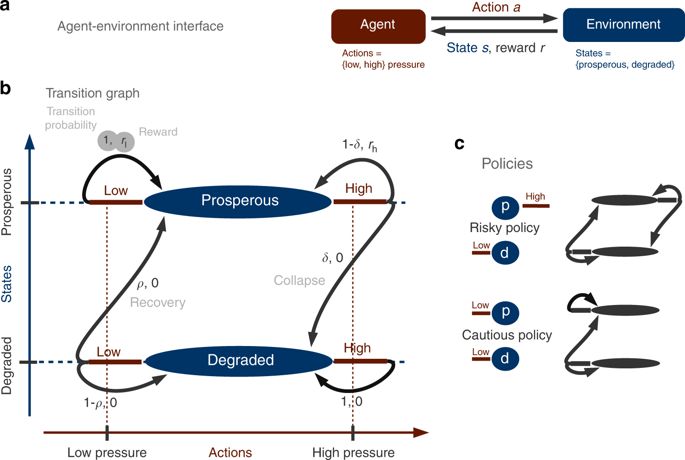
Optimizing economic welfare in environmental governance has been criticized for delivering short-term gains at the expense of long-term environmental degradation. Different from economic optimization, the concepts of sustainability and the more recent safe operating space have been used to derive policies in environmental governance. However, a formal comparison between these three policy paradigms is still missing, leaving policy makers uncertain which paradigm to apply. Here, we develop a better understanding of their interrelationships, using a stylized model of human-environment tipping elements. We find that no paradigm guarantees fulfilling requirements imposed by another paradigm and derive simple heuristics for the conditions under which these trade-offs occur. We show that the absence of such a master paradigm is of special relevance for governing real-world tipping systems such as climate, fisheries, and farming, which may reside in a parameter regime where economic optimization is neither sustainable nor safe.
PIK press release on the paper: better safe than sorry
Reference:
Barfuss, W, Donges, JF, Lade, SJ, Kurths, J (2018),
When optimization for governing human-environment tipping elements is neither sustainable nor safe,
Nature Communications 9, 2354 (2018),
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04738-z,
Official SRC news release.





