Experts meet at Global Solutions Summit in Berlin
06/05/2018 - More than 1100 policy thinkers and policy leaders from all around the world came together recently at the Global Solutions Summit in Berlin to discuss crucial topics for global governance in the context of the next G20 summits in Argentina and Japan. Official delegates from the T20 Argentina and the T20 Japan, Nobel Laureates and high level speakers like German Chancellor Angela Merkel participated in the Berlin Summit of think tanks, policy makers, business leaders and NGOs.
Read More
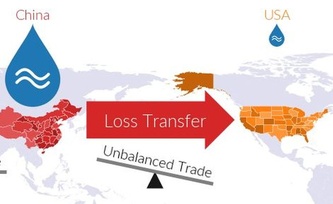
China floods to hit US economy: climate effects through trade chains
05/28/2018 - Intensifying river floods could lead to regional production losses worldwide caused by global warming. This might not only hamper local economies around the globe – the effects might also propagate through the global network of trade and supply chains, a study now published in Nature Climate Change shows. It is the first to assess this effect for flooding on a global scale, using a newly developed dynamic economic model. It finds that economic flood damages in China, which could, without further adaption, increase by 80 percent within the next 20 years, might also affect EU and US industries. The US economy might be specifically vulnerable due to its unbalanced trade relation with China. Contrary to US president Trump’s current tariff sanctions, the study suggests that building stronger and thus more balanced trade relations might be a useful strategy to mitigate economic losses caused by intensifying weather extremes.
Read More
Wealth inequality: closing the gap by taxing land and bequests
22/03/2018 - To reduce wealth inequality without diminishing the economic performance of a country, a policy package of bequest taxes and land value taxes could be the optimal solution. Such a policy package would, in fact, have a strong advantage over corporate taxation, a new study published in the journal International Tax and Public Finance finds. It is the first analysis to include the so far neglected factor of land for tackling wealth inequality. Land is of great interest for studying inequality as climate change might increase land prices and thereby affect housing costs. The cost increase could be countered by smart taxes that would at the same time reduce overall inequality in a country, and hence possibly help to reduce tensions in society that are amplified by populism.
Read More
"Consulted by the Pope": Catholic Academy of Bavaria honours climate economist Edenhofer
05/16/2018 - The Catholic Academy of Bavaria honours the climate economist Ottmar Edenhofer with its Romano Guardini Prize. "As a renowned economist, committed political advisor, and public admonisher, Ottmar Edenhofer has restlessly pointed to climate change as one of the most pressing problems on Earth, and has proposed concrete solutions," the Academy explained. "Not least Pope Francis was seeking Ottmar Edenhofer’s advice repeatedly and intensively for his encyclical Laudato Si. Both are convinced that environmental degradation and poverty are closely intertwined problems that can only be resolved together in the 'concern about our common house'.” Edenhofer is Chief Economist and designated new Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), a member of Leibniz Association; as well he is Director of the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC) and Professor at Technische Universität Berlin (TUB).
Read More
PIK experts at the intersessional climate conference in Bonn
11/05/2018 - In the run-up to this year´s UN climate conference in Katowice in Poland, about 3000 experts and observers met in Bonn to discuss how to implement the Paris Agreement which is to enter into force in 2020. Two key elements of these “intersessionals” were the progress in advancing the Paris Agreement “rulebook”, and the initial in-person phase of the Talanoa dialogue that was introduced at COP23 last year. Several scientists from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) took part in various meetings and presentations in Bonn.
Read More
Bankers, UN and scientists help assess climate risks for finance
04/26/2018 - Together, 16 banks, the United Nations, business consultants and scientists produced first guidance to help the financial industry become more transparent on climate-related risks and opportunities. The report they jointly published, entitled “Extending our horizons”, is based on economic scenarios provided by the Potsdam Instititute for Climate Impact Research, the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, and the International Energy Agency. The innovative methodology will support banks to implement the ground-breaking recommendations of the Financial Stability Board’s Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (FSB TCFD). It focuses on changes that the transition to a low-carbon economy will present to businesses. A complementary report on the physical impacts of climate change for businesses is planned for release in late June.
Read More
Girls'Day: PIK opens up doors and new perspectives to young and female future scientists
26/04/2018 - At this year's Girls'Day, schoolgirls from Berlin and Brandenburg had once again the opportunity to get to know the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and career perspectives in science. About their research on climate change and their work as a researcher at PIK, Levke Caesar and Christina Roolfs reported to the 19 pupils participating. The action day was initiated to open up new career perspectives in mathematical and the natural sciences for girls and young women.
Read More
More than 14.000 Earth scientists meet in Vienna
06/04/2018 - The European Geophysical Union’s (EGU) general assembly in Vienna is one of the world's greatest scientific events – from 8 to 13 April, it attracts more than 14.000 scientists. Numerous experts from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) give talks and participate in debates. A distinguished role is attributed to Stefan Rahmstorf, co-chair of PIK’s Earth System Analysis department, research domain 1. He has been asked to hold the first-ever EGU public lecture at the Vienna Museum for Natural History: “After Paris: Can we still control the climate crisis?”
Read More
Stock-take 2018: Rapid emissions reductions would keep CO2 removal and costs in check
03/29/2018 - Rapid greenhouse-gas emissions reductions are needed if governments want to keep in check both the costs of the transition towards climate stabilization and the amount of removing already emitted CO2 from the atmosphere. To this end, emissions in 2030 would need to be at least 20 percent below what countries have pledged under the Paris climate agreement, a new study finds – an insight that is directly relevant for the global stock-take scheduled for the UN climate summit in Poland later this year. Removing CO2 from the atmosphere through technical methods including carbon capture and underground storage (CCS) or increased use of plants to suck up CO2 comes with a number of risks and uncertainties, and hence the interest of limiting them.
Read More
Enhanced weathering of rocks can help to suck CO2 out of the air – a little
03/06/2018 - Weathering of huge amounts of tiny rocks could be a means to reduce the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. While this is normally a slow natural process during which minerals chemically bind CO2, technological upscaling could make this relevant for so-called negative emissions to help limit climate risks. Yet, the CO2 reduction potential is limited and would require strong CO2 pricing to become economically feasible, according to the first comprehensive assessment of costs and possibilities now published in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Read More
Social and Natural science together: New Co-Directors to lead the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
23/02/2018 - The Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) is reinventing itself – appointing a twin leadership bringing together natural sciences and social sciences stronger than ever. In late September, the German climate economist Ottmar Edenhofer and the Swedish Earth system scientist Johan Rockström will become directors of the internationally renowned institute which is a member of the Leibniz Association. This was decided on Friday by the institute's Board of Trustees, headed by the Brandenburg Ministry of Science, Research and Culture and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. The retirement of the founding director Hans Joachim Schellnhuber this autumn after a quarter of a century as the head of the institute marks the beginning of a new era in Potsdam.
Read More
Coal phase-out: Announcing CO2-pricing triggers divestment
01/29/2018 - Putting the Paris climate agreement into practice will trigger opposed reactions by investors on the one hand and fossil fuel owners on the other hand. It has been feared that the anticipation of strong CO2 reduction policies might – a ‘green paradox’ – drive up these emissions: before the regulations kick in, fossil fuel owners might accelerate their resource extraction to maximize profits. Yet at the same time, investors might stop putting their money into coal power plants as they can expect their assets to become stranded. Now for the first time a study investigates both effects that to date have been discussed only separately. On balance, divestment beats the green paradox if substantial carbon pricing is credibly announced, a team of energy economists finds. Consequently, overall CO2 emissions would be effectively reduced.
Read More
PIK Research Days: “Keep digging in your pockets”
02/23/2018 - Scientists and staff of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) gathered this week for their annual roadshow of scientific achievements and discussions of future projects. Climate negotiations, climate migration, public health, sea-level legacy, jet streams, ice losses at Antarctica, carbon pricing – these were just some of the topics presented by PIK’s four research domains. This year’s research days focused in particular on the upcoming 1.5°C IPCC special report as well as on global change, big data and digitalization.
Read More
Reports of coal’s terminal decline are premature
02/07/2018 - While less new coal-fired power plants are now being built in China and India, the planned expansion in the use of coal in fast-growing emerging economies, such as Turkey, Indonesia and Vietnam, will in part cancel out the reduction. Only if the countries of the world actively counteract this trend, they can achieve the climate goals agreed in the Paris Agreement. These are the results of the study “Reports of coal’s terminal decline may be exaggerated,” authored by researchers from the Potsdam Institute on Climate Impact Research (PIK) and the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC), published in the journal Environmental Research Letters
Read More
National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina appoints Edenhofer
01/31/2018 - Ottmar Edenhofer, Chief Economist at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, was elected member of the Leopoldina. The honouring is a special recognition of his scientific achievements and his personality, said Leopoldina President Jörg Hacker about Edenhofer, who is also Director of the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons (MCC) and Professor of Economics of Climate Change at TU Berlin. The selection of a member for the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina follows strict standards and requires a broad agreement of the Extended Presidium.
Read More
EU commissioner Stylianides visits PIK
01/24/2018 - The European Commissioner for Humanitarian Aid and Crisis Management, Christos Stylianides, visited the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) together with Director-General Monique Pariat and members of cabinet. He was interested in the latest climate research and particularly in prevention measures for the increasing risks of floods and forest fires due to climate change.
Read More
Biomass plantations not compatible with planetary boundaries
01/22/2018 - Planting trees or grasses on a grand scale in plantations to extract CO2 from the atmosphere - this could make a long-term contribution to climate protection, but it would push the planet beyond ecological limits in other dimensions. A new study by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) in the journal Nature Climate Change now for the first time establishes a connection between ambitious international climate objectives and the more comprehensive concept of planetary boundaries. If biomass plantations in which plants bind carbon dioxide during growth are massively expanded, this would entail enormous risks for areas that are already stressed, such as biodiversity, biogeochemical flows, water resources and land use. According to the study, biomass as a means to capture and store CO2 can therefore only make a limited contribution. In order to stabilize the climate, a rapid reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from the combustion of coal, oil and gas is crucial.
Read More
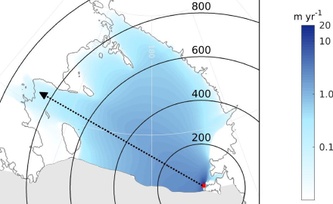
Adaptation now: River flood risks increase around the globe under future warming
11/01/2018 - Rainfall changes caused by global warming will increase river flood risks across the globe. Already today, fluvial floods are among the most common and devastating natural disasters. Scientists have now calculated the required increase in flood protection until the 2040s worldwide, breaking it down to single regions and cities. They find that the need for adaptation is greatest in the US, parts of India and Africa, Indonesia, and in Central Europe including Germany. Inaction would expose many millions of people to severe flooding.
Read More
PIK scientists at the Chaos Communication Congress 34C3
29/12/2017 - For four days between Christmas and New Year´s, thousands of hackers, experts and artists meet every year to exchange news and views and learn about new technological developments and tools. The 34th Chaos Communication Congress (34C3) takes place in Leipzig this year, the organizers expect more than 13.000 participants. Science is represented as well, this year also by experts of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) - climate change is one of this year´s main themes.
Read More
Tiny ice losses at Antarctica’s fringes can accelerate ice loss far away
12/12/2017 - A thinning of small areas of floating ice at Antarctica’s coast can accelerate the movement of ice grounded on rocks hundreds of kilometers away, a new study shows. It is known that the ice shelves surrounding the continent regulate the ice flow from the land into the ocean. So far it was assumed that the ice flow is most vulnerable to melting at the base near the grounding line where the ice flows from land into the sea and becomes afloat. Now scientists found that also melting near the fringes and in the midst of the ice shelves can have direct effects reaching very far inland. This could increase ice loss and hence sea-level rise.
Read More
Transformation to wind and solar could be achieved with low indirect greenhouse gas emissions
12/08/2017 - Different low carbon technologies from wind or solar energy to fossil carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) differ greatly when it comes to indirect greenhouse gas emissions in their life cycle. This is the result of a comprehensive new study conducted by an international team of scientists that is now published in the journal Nature Energy. Unlike what some critics argue, the researchers not only found that wind and solar energy belong to the more favorable when it comes to life-cycle emissions. They also show that a full decarbonization of the global power sector by scaling up these technologies would induce only modest indirect greenhouse gas emissions – and hence not impede the transformation towards a climate-friendly power system.
Read More
Climate and public health: Leopoldina Dialogue in Potsdam
12/05/2017 - Climate change related risks for public health are one of the most important challenges of today. However, the science communities on both sides of the fence have so far not sufficiently interacted to reflect the critical nexus of climate change and health. Taking the first mover advantage, a workshop of the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) now brought together renowned scientists from climate sciences, health and medicine, psychology, environmental sciences, social sciences and economics. They will develop a publication offering stakeholder and decision-makers orientation on public health and climate policy.
Read More
Leibniz Doctorate Award for Leonie Wenz
11/30/2017 - Leonie Wenz from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) receives the Leibniz Doctorate Award 2017 for her dissertation "Climate change impacts in an increasingly connected world". It deals with the consequences of global warming for economic production in the context of an increasingly globalized and interdependent world. "In addition to the scientific quality, which is reflected in several publications in renowned scientific journals, it is also of high social relevance - examplary for Leibniz research," says the Leibniz Association.
Read More
Many PIK scientists at COP23 in Bonn
03/11/2017 - A number of experts from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) will take part in the climate summit COP23, taking place from November 6-17 in Bonn and presided by Fiji. PIK director Hans Joachim Schellnhuber will present the ten things you need to know about climate change, together with UNFCCC´s Patricia Espinosa, for example. At a side event with experts from the ETH Zürich, the ACT Alliance and Bread for the World, PIK´s chief economist Ottmar Edenhofer will discuss how to implement equity in the framework of the Paris Agreement.
Read More
“We need you”: UN climate chief to Potsdam climate scientists
10/13/2017 - Hundreds of millions of people will be affected by climate change impacts and their implications for health or migration already within the next few decades, sectors that so far often get overlooked in this context. This is one of the insights of the Impacts World Conference organised by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) in Germany this week. About 500 scientists from 67 countries were gathering at the conference with the title “Counting the true costs of climate change” to push climate impact research to the next level by better integrating socio-economic factors. At the same time, the institute celebrated its 25th anniversary hosting this meeting of the global impacts research community, in the spirit of its mission followed for a quarter century: further advancing scientific progress and communicating insights to stakeholders.
Read More
Online Course on Climate Change, Risks and Challenges now in English
10/01/2017 - How will climate change affect our lifes? What are the consequences? How can we mitigate climate change? These questions will be explored by scientists from leading German institutes during the interdisciplinary online course ClimateMOOC. The “Massive Open Online Course (MOOC)” is addressed to everybody interested and aims to impart a profound understanding of the climate system and climate change.
Read More
Ending tax breaks after the diesel scandal
09/19/2017 - In response to the diesel scandal, the diesel tax advantage should be completely abandoned within the European Union (EU). In Germany, for example, diesel would then be about 20 cents per liter more expensive at the pump. In return, however, this measure would allow Germany but also France to reduce the emissions of CO2 and nitrogen oxides (NOx) by about 10 percent over five years. This is because diesel drivers in particular are much more sensitive to fuel price changes than previously assumed: a price hike of 20 cents per liter would lower their overall consumption by an estimated 14 percent.
Read More
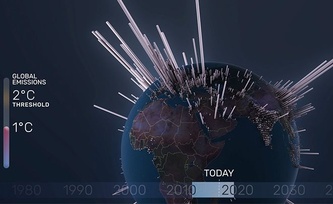
A Brief History of CO2 Emissions – new film online
Extending periods of changing weather, rising sea levels, shifting vegetation zones, even economic losses, social upheaval, and migration of people across the world – these are the effects of global CO2 emissions. The short film “A Brief History of CO2 Emissions” shows how greenhouse gases impact global warming – and our future. The animated short film of the Urban Complexity Lab and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) is now available online.
Read More
Edenhofer ranked as Germany's top climate economist
09/13/2017 Amongst Germany's most important economists Ottmar Edenhofer once again scored excellently in a ranking done by the Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung (FAZ), one of the country's most influential newspapers. He turned out to be the only researcher investigating climate and environmental issues in the group of top economists. For the third time in a row he improved, moving up to the 11th rank this year.
Read More
Potsdam Summer School explores the future of cities
09/04/2017 - The rapid pace of change around the world is presenting humankind and human environments with tremendous challenges. What solutions and strategies can we employ to future-proof our cities in the age of climate change? Experts from 30 countries will meet to discuss these issues with leading sustainability researchers at the 2017 Potsdam Summer School on 4 – 13 September. Their findings will be presented to the public in a memorandum on 13 September.
Read More