| case: | EU3 | location: | Europe | sectors: | Forestry | interactive maps |
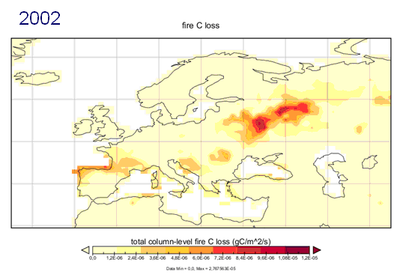
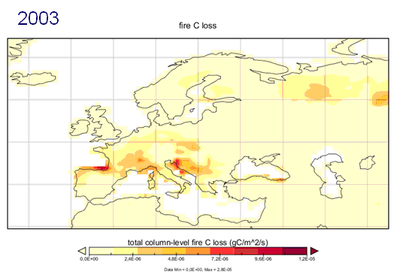
Forest fires are one of the main disturbances affecting carbon sequestration of European forests and also leading to loss of life. Although it is generally recognized that the occurrence of forest fires in Europe is due mainly to causes of an anthropogenic nature, year to year fire risk is also linked to weather conditions.
|
|
|
Figure 1 - Map of carbon losses related to forest fires in Europe for June-August 2002 and 2003. Maps were obtained using the Community Land Model (CLM) 4.0. Website: http://www.cgd.ucar.edu/tss/clm/
|
|