FirEUrisk: PIK joins EU project to analyze and manage wildfires
06/03/2021 - The Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), along with 38 partner institutions from 19 countries, will develop a science-based strategy to manage, monitor and analyze major forest fires in Europe. Funded by the European Union, the FirEUrisk project brings together researchers, practitioners, policymakers and citizens to study the vulnerability and resilience of communities and countries to wildfires in Northern, Central and Mediterranean Europe. The overarching goal of the project is to adapt fire management strategies to expected climate and socio-economic changes.
Read More
Science podcast launched: "Sustain Ability. The Potsdam Dialogues"
05/18/2021 - Science for your ears: The Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) has launched its very own podcast. The dialogue series ‘Sustain Ability. The Potsdam Dialogues - Science for a Safe Tomorrow’ brings together leading thinkers and doers to discuss how to stabilize our climate and advance the transition to sustainability. The first episode features EU Commission Vice President Frans Timmermans and PIK Director Johan Rockström.
Read More
Few realistic scenarios left to limit global warming to 1.5°C
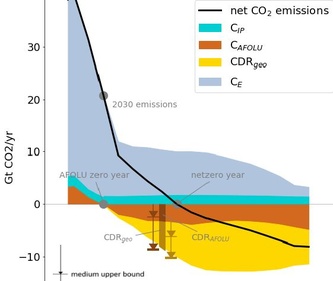
05/14/2021 - Of the over 400 climate scenarios assessed in the 1.5°C report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), only around 50 scenarios avoid significantly overshooting 1.5°C. Of those only around 20 make realistic assumptions on mitigation options, for instance the rate and scale of carbon removal from the atmosphere or extent of tree planting, a new study shows. All 20 scenarios need to pull at least one mitigation lever at "challenging" rather than "reasonable" levels, according to the analysis. Hence the world faces a high degree of risk of overstepping the 1.5°C limit. The realistic window for meeting the 1.5°C target is very rapidly closing.
Read More
Climate change is making it harder to get a good cup of coffee
04/14/2021 - Ethiopia may produce less specialty coffee and more rather bland tasting varieties in the future. This is the result of a new study by an international team of researchers that looked at the peculiar effects climate change has on Africa's largest coffee producing nation. Their results are relevant both for the country's millions of smallholder farmers, who earn more on specialty coffee than on ordinary coffee, as well as for baristas and coffee aficionados around the world.
Read More
The future of Lower Saxony: Expert report with PIK participation published
03/25/2021 - Climate change, advancing digitalization and demographic changes: These are just three examples of current social challenges for the future of Lower Saxony. On the initiative of the state government, an independent scientific commission with various researchers - including PIK researcher Hermann Lotze-Campen - has developed recommendations for the state. Today, the Commission Niedersachsen 2030 handed over its prepared report to the state government.
Read More
When the flames are out, danger continues: Cascading effects of wildfires
03/15/2021 - After extreme weather events like droughts and wildfires, it often only takes small additional natural hazards like rainfall to trigger further disastrous cascading hazards, a new study finds. A team of scientists based in Potsdam and Berlin analyzed the devastating forest fires in Australia from 2019 to 2020, which - in their intensity and severity – are likely linked to human-made global warming. The researchers reveal that the following much needed rain caused severe further damage, gravely impacting both people and nature.
Read More
Limiting water stress risks: irrigation management key for bioenergy production to mitigate climate change
03/08/2021 - To avoid a substantial increase in water scarcity, biomass plantations for energy production need sustainable water management, a new study shows. Bioenergy is frequently considered one of the options to reduce greenhouse gases for achieving the Paris climate goals, especially if combined with capturing the CO2 from biomass power plants and storing it underground. Yet growing large-scale bioenergy plantations worldwide does not just require land, but also considerable amounts of freshwater for irrigation – which can be at odds with respecting Earth’s Planetary Boundaries. Scientists now calculated in their to date most detailed computer simulations how much additional water stress could result for people worldwide in a scenario of conventional irrigation and one of sustainable freshwater use.
Read More
Farmers in focus: Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on crops
12/11/2020 - Agriculture is a key socio-economic sector that both influences the climate and is exposed to climate impacts. To reach targets on food security, protection of biodiversity and the natural environment as well as on climate mitigation for the global common land, it is crucial to know how and where climate change and increasing atmospheric concentrations of CO2 affect crops. Decision makers and farmers need to quantify the risks to their sector and evaluate sustainable adaptation and mitigation strategies. An international team of agro-climatic experts, including PIK researcher Christoph Müller, has reviewed existing crop models that are used for these climate change risk assessments: While the size of CO2 fertilization effects is still uncertain to some extent, their results, published in Nature Food today, suggest that presenting crop modelling results without accounting elevated CO2 simulations are obsolete and don't offer added value to decision makers.
Read More
Low food prices, high energy use: The pros and cons of emerging technology in our food system
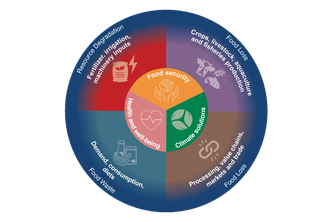
12/08/2020 - An international team of scientists, including PIK researchers, has identified the potential impacts emerging from food system technologies in relation to the Sustainable Development Goals. In a new study, that has been published in Lancet Planetary Health, they find that while new technologies and innovation can help fix some issues with the food system, they also have far-reaching impacts. These can cause disruption and unintended consequences, some beneficial and some not, for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Food system innovation will be key to succeed, but new technologies need to be guided by science-based targets to avoid trade-offs and rebound effects.
Read More
FABLE Report 2020: Pathways to sustainable land-use and food systems
The Food, Agriculture, Biodiversity, Land-Use, and Energy (FABLE) Consortium has presented an updated plan on how countries can meet mid-century objectives on food security, healthy diets, greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity, forest conservation, and freshwater use. In part coordinated by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), FABLE's mission is to mobilize top knowledge institutions from 20 countries to support the development of decision-support tools and long-term pathways towards sustainable food and land-use systems.
Read More
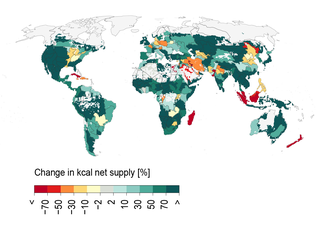
Starved, stuffed and squandered: New study reveals consequences of decades of global nutrition transition
11/18/2020 - Just a handful of rice and beans – a part of our world is starved. Hawaiian Pizza and ice-cream – another part of our world is stuffed, throwing away food every day. This gap is likely to worsen, while food waste will increase and pressure on the environment will go up, a new study shows. Researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) assessed the consequences if the current nutrition transition, from scarce starch-based diets towards processed foods and animal products, continues – the calculations combine, for the first time, estimates for under- and overweight, food composition and waste. Their findings provide a startling look ahead: By 2050, more than 4 billion people could be overweight, 1.5 billion of them obese, while 500 million people continue to be underweight.
Read More
Larger part of Amazon rainforest at risk of tipping
10/05/2020 A larger part of the Amazon rainforest than previously thought is at risk of crossing a tipping point where it could become a savanna-type ecosystem, according to a new study. The research, based on computer models and data analysis, is published by a team of scientists including Johan Rockström, Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, in the journal Nature Communications. Rainforests are very sensitive to changes that affect rainfall for extended periods. If rainfall drops below a certain threshold, areas may shift into a savanna state.
Read More
Indian monsoon can be predicted better after volcanic eruptions
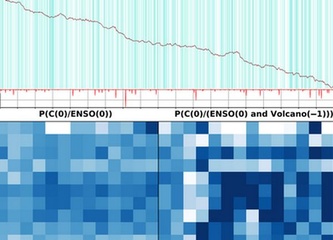
09/18/2020 - Large volcanic eruptions can help to forecast the monsoon over India – the seasonal rainfall that is key for the country’s agriculture and thus for feeding one billion people. As erratic as they are, volcanic eruptions improve the predictability, an Indian-German research team finds. What seems to be a paradox is in fact due to a stronger coupling between the monsoon over large parts of South and South-East Asia and the El Niño phenomenon after an eruption. Combining data from meteorological observations, climate records, computer model simulations, and geological archives such as tree-rings, corals and ice-cores from past millennia of Earth history, the researchers found that a synchronization of the monsoon with the strongest mode of natural climate variability, the El Niño, makes it easier to anticipate the strength of seasonal rainfall in the Indian subcontinent.
Read More
Reversing the Loss of Biodiversity: Researchers Present Ambitious Plan
09/10/2020 - The rapid extinction of animal and plant species could be reversed by 2050 – by doing two things: Investing in better land-use management and transforming agriculture and the food industry. A new study by an international team of scientists, including Hermann Lotze-Campen, Alexander Popp, and Florian Humpenöder from the Potsdam-Institute for Climate Impact Research, lays out what it will take to reverse the current alarming trends of biodiversity loss – without endangering other important Sustainable Development Goals set by the United Nations General Assembly.
Read More
World Food Convention 2020 features keynote by Professor Lotze-Campen on food security
06/24/2020 - The Covid-19 pandemic has shown the volatility of our global food supply. In his keynote "Cooperation, preparation, information – how to prepare the food system for economic shocks", Professor Hermann Lotze-Campen, Head of PIK’s Climate Resilience Department, will contribute to this year's annual World Food Convention by addressing the crucial role international collaboration plays for averting future hunger crises in the wake of climate-related disasters.
Read More
From artificial meat to fine-tuning photosynthesis: Food System Innovation – and how to get there
19/05/2020 - Food production has always shaped the lives of humans and the surface of the Earth. Be it plough or refrigerator, time and again innovations have transformed the ways we grow, process, and consume food over the last millennia. Today, with almost 40 per cent of all land on Earth used for food production, the food system massively impacts climate and environment – from nitrogen flows to water use, from biodiversity to greenhouse gas emissions. In a new study published in the journal NatureFOOD, an international team of researchers has now assessed and categorised key innovations with a potential to transform the food system, from artificial meat or seafood to biofortified crops or improved climate forecasts – and established what is most needed to make them succeed.
Read More
From forests to peatlands: once lost, ecosystem carbon stores might not be recoverable in time
01/04/2020 - Huge amounts of carbon are stored in ecosystems like peatlands, mangroves, old-growth forests and marshes, which play a crucial role for our Earth system. Once released due to land use changes like the conversion to agriculture, this carbon could be not be recoverable within time to avoid global warming beyond 1,5 degrees Celsius, a new study led by Conservation International shows. Johan Rockström, Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, is one of the authors. These land areas should be particularly protected, the researchers argue in the journal Nature Climate Change.
Read More
Regional nuclear war a risk for global food security
16/03/2020 - Even a limited nuclear war could have dangerous effects far beyond the region that is fatally hit. It would result in global cooling that substantially reduces agricultural production in the world’s main breadbasket regions, from the US, to Europe, Russia, and China. The particular effect on food security worldwide including trade responses has now for the first time been revealed by an international team of scientists in a study based on advanced computer simulations. The sudden temperature reduction would lead to a food system shock unprecedented in documented history. It would not undo long-term climate change from fossil fuels use, though – after about a decade of cooling, global warming would surge again.
Read More
Managing forests in the 21st century: Experts gather at PIK
06/03/2020 - Forests all over Europe feel the pressure from ongoing climate change, yet at the same time provide a wide range of resources to mitigate and to adapt to global warming. Smartly targeted management of forest is thus key, finds an international gathering of leading experts hosted by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research this week. More than 100 scientists from institutions ranging from German National Park Berchtesgarden to US Oregon State University and Russian Higher School of Economics participated in three days of intense discussions and a field trip, more than 30 additional participants joined via videolink.
Read More
Ricarda Winkelmann departs on “Expedition Anthropocene“ on Mount Chimborazo, Ecuador
24/02/2020 – Humans are the defining geological force shaping Earth in our current epoch that has been named the Anthropocene. Across disciplinary boundaries, six members of the 'Junge Akademie', the academy of prominent young scientists and artists from German speaking backgrounds, have departed on an expedition on tracing some of human’s impact onto the environment. 200 years after Alexander von Humboldt, they will climb the Ecuadorian volcano Chimborazo in search of humanity’s footprint in different altitudes and vegetation zones. Besides PIK’s Ricarda Winkelmann, a mathematician glaciologist, the scientists involved come from a great variety of disciplinary backgrounds: biology, chemistry, sound ecology, computer science, and medicine.
Read More
Focus on food to address climate change
18/02/2020 - Bringing together agricultural production, supply chains, and consumption: In a comment published in the new journal Nature Food researchers discuss a new global food system approach to climate change research. When these activities are considered together, they represent 21 to 37 percent of total human-caused greenhouse gas emissions, the authors note. This new approach also enables a fuller assessment of the vulnerability of the global food system to increasing droughts, intensifying heatwaves, heavier downpours, and exacerbated coastal flooding. Food system responses thus play a major role in both adapting to and mitigating climate change, the authors assert.
Read More
Buildings can become a global CO2 sink if made out of wood instead of cement and steel
A material revolution replacing cement and steel in urban construction by wood can have double benefits for climate stabilization, a new study shows. First, it can avoid greenhouse gas emissions from cement and steel production. Second, it can turn buildings into a carbon sink as they store the CO2 taken up from the air by trees that are harvested and used as engineered timber. However while the required amount of timber harvest is available in theory, such an upscaling would clearly need most careful, sustainable forest management and governance, the international team of authors stresses.
Read More
Rockström as one Voice of Science at Davos World Economic Forum
21/01/2020 – After a year of climate change making headlines, the global leaders’ meeting at the World Economic Forum in Davos, too, has climate change written in large letters on its programme. Johan Rockström, Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research is one of the scientists present to make the voice of science heard.
Read More
Tipping mechanisms could spark profound societal change towards climate stabilization: new study
21/01/2020 - Limiting global warming to well below 2°C requires a decarbonized world by 2050 at the latest and a corresponding global transformation of the energy and land use systems of societies across the world. To achieve this goal of net-zero carbon by 2050 emissions need to be cut by half every decade from now on. An interdisciplinary team of researchers now explored tipping mechanisms that have the potential to spark rapid yet constructive societal changes towards climate stabilization and overall sustainability. These tipping elements and mechanisms could bring about a transition that is fast enough for meeting the targets of the Paris climate agreement. Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) the scientists identify six socio-economic tipping elements and related interventions that could bring such a transition to a deep and rapid global decarbonization on its way.
Read More
Feeding the world without wrecking the planet is possible
20/01/2020 - Almost half of current food production is harmful to our planet – causing biodiversity loss, ecosystem degradation and water stress. But as world population continues to grow, can that last? A study led by researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) now suggests a comprehensive solution package for feeding 10 billion people within our planet’s environmental boundaries. Supplying a sufficient and healthy diet for every person whilst keeping our biosphere largely intact will require no less than a technological and socio-cultural U-turn. It includes adopting radically different ways of farming, reduction of food waste, and dietary changes. The study's publication coincides with the World Economic Forum in Davos and the International Green Week in Berlin, the world's biggest food and agriculture fair.
Read More
Climate change, food and agriculture: PIK expertise at International Green Week in Berlin
20/01/2020 - Hundreds of thousands of people are currently exploring the International Green Week in Berlin, a leading global trade fair for agriculture and food with featuring more than 1800 exhibitors from 72 countries. According to the organizers, the International Green Week 2020 is focusing on climate change like never before, with numerous exhibitions and events. This year's trend topics include sustainability, resource conservation and environmentally friendly production processes. Experts from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) will also be present at events at the Green Week from 17-26 January.
Read More
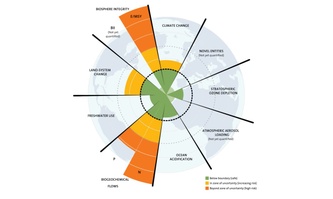
Planetary boundaries: Interactions in the Earth system amplify human impacts
16/12/2019 - What we do to one part of our Earth system does not just add to what we do to other parts – transgressing one planetary boundary can amplify human impacts on another one. For the first time, an international team of scientists now quantified some of the planetary-scale interactions in the Earth system. These biophysical interactions have in fact almost doubled direct human impacts on the nine planetary boundaries, from climate change to freshwater use. This insight can now be applied in policy design for safeguarding the livelihoods of generations to come.
Read More
Global food production at risk of simultaneous heat waves across breadbasket regions
09/12/2019 - Certain patterns in the jet stream encircling the Earth can bring simultaneous heatwaves to breadbasket regions responsible for up to a quarter of global food production. Particularly susceptible are Western North America, Western Europe, Western Russia and Ukraine. Extreme weather events of such extent can significantly harm food production and thus make prices soar. In recent years, major food price spikes were associated with social unrest.
Read More
Decarbonizing the power sector: renewable energy offers most benefits for health and environment
19/11/2019 - Electricity supply is one of the biggest CO2 emitters globally. To keep global warming well below 2°C, several paths lead to zero emissions in the energy sector, and each has its potential environmental impacts - such as air and water pollution, land-use or water demand. Using a first-time combination of multiple modelling systems, an international team of researchers led by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) has now quantified the actual benefits and downsides of three main roads to decarbonisation. They show that relying mainly on wind and solar would bring most co-benefits for the health of people and planet. Switching to carbon capture and storage in combination with fossil and biomass resources, in turn, is likely to convey significant environmental costs by devouring large areas at the cost of biodiversity, and by releasing pollutants to the environment.
Read More
Johan Rockström Chairs Newly Launched Earth Commission
19/09/2019 - The initiative of 20 globally renowned scientists on Earth Systems sets out to identify the concrete risks climate change brings for cities and firms. They aim to delineate the exact scientific borders of what our Planet can bear in terms of human-made climatic changes. Specifically, the commission will elaborate concrete tangible targets for cities and firms, thus scientifically underpinning tailored Goals for Land, Water, Oceans, and Biodiversity.
Read More