Ice loss due to warming leads to warming due to ice loss: a vicious circle
10/27/2020 - The loss of huge ice masses can contribute to the warming that is causing this loss and further risks. A new study now quantifies this feedback by exploring long-term if-then-scenarios. If the Arctic summer sea-ice were to melt completely, a scenario that is likely to become reality at least temporarily within this century with ongoing greenhouse gas emissions from burning fossil fuels, this could eventually add roughly 0.2°C to global warming. This is, however, not in addition to IPCC projections of future warming since these already take the relevant mechanisms into account. Still, the scientists could now separate the effects of the ice loss from other effects and quantify it. The 0.2°C are substantial, given that global mean temperature is currently about one degree higher than in pre-industrial times, and governments worldwide agreed to stop the increase well below two degrees.
Read More
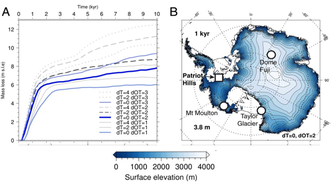
Stability Check on Antarctica Reveals High Risk for Long-Term Sea-Level Rise
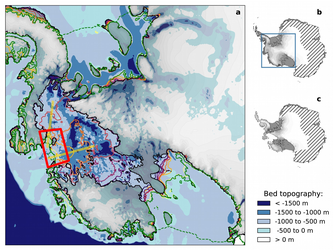
09/23/2020 - The warmer it gets, the faster Antarctica loses ice – and much of it will then be gone forever. Consequences for the world’s coastal cities and cultural heritage sites would be detrimental, from London to Mumbai, and from New York to Shanghai. That’s what a team of researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Potsdam University and New York’s Columbia University has found out in their new study, published in Nature (cover story), on how much warming the Antarctic Ice Sheet can survive. In around one million hours of computation time, their unprecedentedly detailed simulations delineate where exactly and at which warming levels the ice would become unstable and eventually melt and drain into the ocean. They find a delicate concert of accelerating and moderating effects, but the main conclusion is that unmitigated climate change would have dire long-term consequences: If the global mean temperature level is sustained long enough at 4 degrees above pre-industrial levels, Antarctic melting alone could eventually raise global sea levels by more than six meters.
Read More
Berlin Climate and Security Conference Kicks Off Major New Risk Assessment
06/23/2020 - Climate destabilization increases risks to peace and security - to address these risks, scientists and policy-makers are teaming up to find solutions. The Berlin Climate and Security Conference (BCSC) is the global meeting place for leaders from governments, international organisations, the scientific community, the private sector and civil society to explore how climate change is impacting peace and security—and what action the international community can take to tackle climate-fragility risks. This year the high-level event, which features statements from over 14 foreign ministers, heads of state, and UN chiefs, explores the steps necessary to ensure we build a climate- and conflict-sensitive post-Covid world. It is organised by the German Federal Foreign Office, in partnership with adelphi and Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK).
Read More
Museum für Naturkunde & PIK launch Summer School for Climate Knowledge
06/19/2020 - At the Museum für Naturkunde Berlin, interested guests can use the summer holidays to strengthen their knowledge of the climate and its effects - and young people from all over Germany can take part online. The summer school is taking place in cooperation with researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), and for the first time digitally. The easy-to-understand lectures and workshops complement each other, but can also be attended individually.
Read More
Federal Government reappoints Wolfgang Lucht to the German Advisory Council
10.06.2020 - The German government has reappointed Wolfgang Lucht to its German Advisory Council on the Environment. Lucht is co-head of the Earth System Analysis Department at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and has been a member of the Council for the past four years. Only a few days ago, the seven-member Council submitted a report of several hundred pages - which is only published every four years - to the Federal Minister for the Environment, Svenja Schulze. The committee of professors repeatedly takes a critical stance on current issues and thus advises the government.
Read More
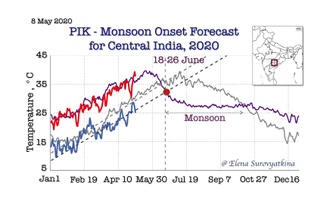
Delayed monsoon onset in Central India: early warning forecast
12/05/2020 - Summer Monsoon in Central India will likely begin between 18th and 26 of June, according to the new early forecast developed at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). Led by PIK expert Elena Surovyatkina, the Monsoon forecast method showed to be successful already four years in a row. With global warming the monsoon is changing, breaking well-established “rules” of the phenomenon and thus becoming more unpredictable. A raising demand for a new understanding of the Indian Monsoon in order to be better prepared makes long-term forecasting even more important.
Read More
Sea level could rise more than 1 metre by 2100 if emission targets are not met, reveals survey amongst 100 experts
08/05/2020 - Global mean sea-level rise could exceed 1 metres by 2100 and 5 metres by 2300 with unchecked emissions, a survey among 100 leading international experts finds. The risk assessment is based on the increasing body of knowledge of the systems involved – while the scientists highlight the remaining uncertainties, they say it is clear now that previous sea-level rise estimates have been too low. The study led by scientists of Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) appears today in the Nature partner journal Climate and Atmospheric Science.
Read More
Climate disasters increase risks of armed conflicts: new evidence
02/04/2020 - The risk for violent clashes increases after weather extremes such as droughts or floods hit people in vulnerable countries, an international team of scientists finds. Vulnerable countries are characterized by a large population, political exclusion of particular ethnic groups, and low development. The study combines global statistical analysis, observation data and regional case study assessments to yield new evidence for policy-makers.
Read More
Homeschooling: Researchers support online learning with explanatory videos
01/04/2020 - As schools are closed due to the corona crisis, the Potsdam Institute offers special online lectures for children and young people as a small contribution to learning at home. Explanatory videos conveying some basics about the climate are intended to provide inspiration for the many hours spent at the desk at home instead of in the classroom. The films are created by the scientists themselves - a little handout from the research team in home office to young viewers in home schooling.
Read More
The Climate Crisis and Churches' Options for Action: Ecumenical Learning Journey to PIK
05/03/2020 - 32 representatives from several churches took on a leaning journey about climate change and its consequences in Berlin and Potsdam. At the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Wolfgang Lucht shared some insights on Earth system research. The participants' conclusion: The church can play a major role in bridging the gap between knowledge and action and contribute to a different lifestyle through ecological spirituality.
Read More
Ricarda Winkelmann departs on “Expedition Anthropocene“ on Mount Chimborazo, Ecuador
24/02/2020 – Humans are the defining geological force shaping Earth in our current epoch that has been named the Anthropocene. Across disciplinary boundaries, six members of the 'Junge Akademie', the academy of prominent young scientists and artists from German speaking backgrounds, have departed on an expedition on tracing some of human’s impact onto the environment. 200 years after Alexander von Humboldt, they will climb the Ecuadorian volcano Chimborazo in search of humanity’s footprint in different altitudes and vegetation zones. Besides PIK’s Ricarda Winkelmann, a mathematician glaciologist, the scientists involved come from a great variety of disciplinary backgrounds: biology, chemistry, sound ecology, computer science, and medicine.
Read More
2°C ocean warming has been enough to destabilize Antarctica in the past
12/02/2020 - A melting of the Antarctic ice sheets would have far-reaching consequences for sea-level rise and coastal regions around the world. Based on new data from the Antarctic ice, an international team of scientists now reveals how the ice sheet reacted to rising temperatures in the past. Published in the US Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, their study using data from a blue ice field shows for the first time that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet already proved to be quite unstable during the last warm period 120,000 years ago. The Eemian warm period was the last phase of climate history with global temperatures similar to those that the world is heading towards due to manmade global warming in the coming decades.
Read More
Tipping mechanisms could spark profound societal change towards climate stabilization: new study
21/01/2020 - Limiting global warming to well below 2°C requires a decarbonized world by 2050 at the latest and a corresponding global transformation of the energy and land use systems of societies across the world. To achieve this goal of net-zero carbon by 2050 emissions need to be cut by half every decade from now on. An interdisciplinary team of researchers now explored tipping mechanisms that have the potential to spark rapid yet constructive societal changes towards climate stabilization and overall sustainability. These tipping elements and mechanisms could bring about a transition that is fast enough for meeting the targets of the Paris climate agreement. Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) the scientists identify six socio-economic tipping elements and related interventions that could bring such a transition to a deep and rapid global decarbonization on its way.
Read More
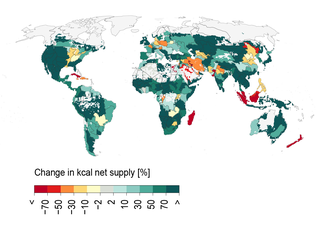
Feeding the world without wrecking the planet is possible
20/01/2020 - Almost half of current food production is harmful to our planet – causing biodiversity loss, ecosystem degradation and water stress. But as world population continues to grow, can that last? A study led by researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) now suggests a comprehensive solution package for feeding 10 billion people within our planet’s environmental boundaries. Supplying a sufficient and healthy diet for every person whilst keeping our biosphere largely intact will require no less than a technological and socio-cultural U-turn. It includes adopting radically different ways of farming, reduction of food waste, and dietary changes. The study's publication coincides with the World Economic Forum in Davos and the International Green Week in Berlin, the world's biggest food and agriculture fair.
Read More
Australian bush fires: "What is happening in the southeast of Australia right now is breaking all records"
10/01/2020 - Australia is burning. In a statement, Kirsten Thonicke, expert for fire ecology and forests at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), explains the causes and how the devastating fires are related to man-made climate change.
Read More
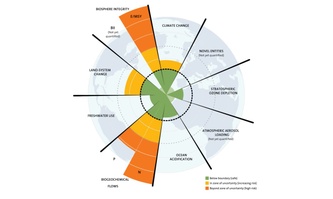
Planetary boundaries: Interactions in the Earth system amplify human impacts
16/12/2019 - What we do to one part of our Earth system does not just add to what we do to other parts – transgressing one planetary boundary can amplify human impacts on another one. For the first time, an international team of scientists now quantified some of the planetary-scale interactions in the Earth system. These biophysical interactions have in fact almost doubled direct human impacts on the nine planetary boundaries, from climate change to freshwater use. This insight can now be applied in policy design for safeguarding the livelihoods of generations to come.
Read More
Global food production at risk of simultaneous heat waves across breadbasket regions
09/12/2019 - Certain patterns in the jet stream encircling the Earth can bring simultaneous heatwaves to breadbasket regions responsible for up to a quarter of global food production. Particularly susceptible are Western North America, Western Europe, Western Russia and Ukraine. Extreme weather events of such extent can significantly harm food production and thus make prices soar. In recent years, major food price spikes were associated with social unrest.
Read More
COP25: PIK experts in Madrid
02.12.2019 - "Time for Action": About 25,000 delegates from all over the world are expected to attend the UN Climate Conference COP25 from December 2-13 in Madrid, Spain. "We stand at a critical juncture in our collective efforts to limit dangerous global heating", UN General Secretary António Guterres said at the Opening Ceremony of COP25 in the Spanish Capital. "Millions throughout the world – especially young people – are calling on leaders from all sectors to do more, much more, to address the climate emergency we face. They know we need to get on the right path today, not tomorrow. That means important decisions must be made now," he stressed in his remarks.
Read More
Ten PIK researchers among the most influential scientists worldwide: ranking
29.11.2019 - According to a new Clarivate ranking, ten scientists from all research areas of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) are among the most cited researchers worldwide. This places them among the most influential scientists in the world, and their studies rank among the top 1% of scientific literature. Whether natural or social sciences, PIK is among the most renowned research institutions in Germany and worldwide, as the recently published ranking shows.
Read More
Climate tipping points – too risky to bet against
28/11/2019 - From the Greenland and West-Antarctic ice sheets to coral reefs or the Amazon rainforest – a number of critical elements in the Earth system could be more likely to tip than was previously thought, a group of leading scientists warns in in the highly renowned journal Nature. Evidence is mounting that these events are also more interconnected, which could eventually lead to domino effects. A possible tipping cascade of irreversible changes might put the livelihoods of people around the world at risk and marks a state of planetary emergency, the authors argue in their comment.
Read More
Early warning: Physicists from Giessen, Potsdam and Tel Aviv forecast "El Niño" for 2020
04/11/2019 -The serious weather phenomenon "El Niño" could soon occur again in the Pacific region. Researchers at Justus Liebig University Giessen (JLU), the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel, find that there will probably be another "El Niño" by the end of 2020. The prediction models commonly used do not yet see any signs of this.
Read More
"Uncomfortable truths need freedom" - Researcher Winkelmann at Alliance of Science Organisations with Federal President Steinmeier
27/09/2019 - Science should interfere, said Federal President Frank-Walter Steinmeier at the closing event of the campaign "Freedom is our System". The campaign was led by the Alliance of Science Organisations under the leadership of the Leibniz Association. The physicist Ricarda Winkelmann from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) also spoke at the event in Berlin's Futurium.
Read More
Leibniz PhD General Assembly gathers at PIK
26/09/2019 - PhD students from all disciplines of the Leibniz Association are gathering this week in Potsdam to discuss their research, exchange ideas and network. Hosted by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), the two day Leibniz PhD Network General Assembly brings together doctoral researchers for an elaborate programme including talks, discussions and the election of spokespersons. The students were welcomed by Ingo Bräuer, head of PIK's science coordination and transfer, at PIK on Telegrafenberg Science Campus.
Read More
Sea level rise: West Antarctic ice collapse may be prevented by snowing ocean water onto it
18/07/2019 - The ice sheet covering West Antarctica is at risk of sliding off into the ocean. While further ice-sheet destabilisation in other parts of the continent may be limited by a reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, the slow, yet inexorable loss of West Antarctic ice is likely to continue even after climate warming is stabilised. A collapse might take hundreds of years but will raise sea levels worldwide by more than three meters. A team of researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) is now scrutinising a daring way of stabilising the ice sheet: Generating trillions of tons of additional snowfall by pumping ocean water onto the glaciers and distributing it with snow canons. This would mean unprecedented engineering efforts and a substantial environmental hazard in one of the world’s last pristine regions – to prevent long-term sea level rise for some of the world’s most densely populated areas along coastlines from the US to China.
Read More
Environment Council presents new special report on the legimitimacy of environmental policy
27.06.2019 - In its new special report, the German Advisory Council on the Environment (SRU) discusses the legitimacy of environmental policy and proposes institutional developments for policy and administration. The 300-page paper is entitled "Democratic governance within ecological boundaries - on the legimitation of environmental policy". Against the background of long-term and systemic environmental problems, the members explain how a the state is not only legitimised to act but also obliged, to preserve people's livelihoods. The report was presented to Federal Environment Minister Svenja Schulze in Berlin.
Read More
"Heat waves are on the rise": PIK statement
24/06/2019 - Germany likely faces a heat wave this week. In which way is this releated to human-caused climate change?
Read More
CO2-pricing: German chancellor Angela Merkel visited PIK for a scientific briefing
14/06/2019 - For more than two hours, German Chancellor Angela Merkel visited the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) last Thursday, June 13th, to discuss climate change and climate policy with Director Ottmar Edenhofer and other researchers. A special focus of the meeting lay on options for an effective and fair CO2 pricing. Besides Mrs Merkel, Minister of State to the Federal Chancellor, Helge Braun, spokesman State Secretary Steffen Seibert and experts from the Chancellery also took part. A good two dozen researchers from all research departments at PIK were involved in the round table discussion taking place the Great Cupola of PIK's historic Michelson building and presented research results on climate risks and possible solutions for the climate crisis.
Read More
Lucht at meeting of all CDU/CSU parliamentary group leaders
06/04/2019 - The German conservative party CDU/CSU is re-thinking climate policy. The elected representatives invited experts Wolfgang Lucht from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and Patrick Graichen from the Agora Energiewende to the two-day conference of all parliamentary group chairmen - from the state parliaments in the German "Länder" to the federal level in the Bundestag and the European Parliament - this week in Weimar. They discussed risks of human-made global warming, from extreme weather events to changing our landscapes, as well as the possibilities for an effective reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The conference was also attended by German Chancellor Angela Merkel and Bavarian Prime Minister Markus Söder.
Read More
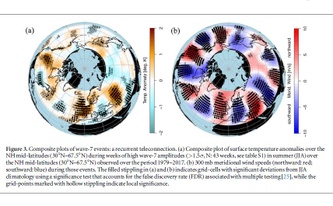
Summer extremes of 2018 linked to stalled giant waves in jet stream
29/04/2019 - Record breaking heatwaves and droughts in North America and Western Europe, torrential rainfalls and floods in South-East Europe and Japan - the summer of 2018 brought a series of extreme weather events that occurred almost simultaneously around the Northern Hemisphere in June and July. These extremes had something in common, a new study by an international team of climate researchers now finds: the events were connected by a newly identified pattern of the jet stream encircling the Earth. The jet stream formed a stalled wave pattern in the atmosphere which made weather conditions more persistent and thus extreme in the affected regions. The same pattern also occurred during European heat waves in 2015, 2006 and 2003, which rank among the most extreme heatwaves ever recorded. In recent years, the scientists observed a clear increase of these patterns.
Read More
Dutch royal couple visits Telegrafenberg
05/22/2019 - King Willem-Alexander and Queen Máxima of the Netherlands visited the Albert Einstein Science Park on Potsdam's Telegrafenberg during their stay in the State of Brandenburg today. In the presence of Brandenburgs Prime Minister Dietmar Woidke and Minister of Science Martina Münch, the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and the GeoResearchCenter (GFZ) signed cooperation agreements with Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam and TU Delft. The agreements are on geothermal research and research on weather extremes.
Read More